ഹിന്ദുസ്താനി ഭാഷ
വടക്കേ ഇന്ത്യയിലും പാകിസ്താനിലും സംസാരിക്കപ്പെടുന്ന ഭാഷകളുടെ മിശ്രമായ ഒരു ഭാഷ (lingua franca) ആണ് ഹിന്ദുസ്താനി (हिन्दुस्तानी , ہندوستانی ) അഥവാ ഹിന്ദി-ഉർദു (हिंदी उर्दू |ہندی اردو) [6][7] ദില്ലിയിൽ സംസാരിക്കപ്പെടുന്ന ഖഡിബോലിയിൽനിന്നും ഉരുത്തിരിഞ്ഞുണ്ടായ ഹിന്ദുസ്ഥാനിയിൽ സംസ്കൃതം, പേർഷ്യൻ, അറബി എന്നീ ഭാഷകളിൽനിന്നും കടംകൊണ്ട പദങ്ങൾ വളരെയേറെയുണ്ട്.[8][9] [10] ഹിന്ദുസ്ഥാനി അടിസ്ഥാനമായുള്ള രണ്ട് ഔദ്യോഗികഭാഷകൾ ഹിന്ദി, ഉർദു എന്നിവയാണ്.
| ഹിന്ദുസ്താനി | |
|---|---|
| हिन्दुस्तानी, ہندوستانی Hindustānī | |
 | |
| Native to | ഇന്ത്യ , പാകിസ്താൻ. |
| Region | ദക്ഷിണേഷ്യ |
Native speakers | Native: 240 million (1991-1997)[1] Second language: 165 million (1999)[2] Total: 490 million (2006)[3] |
Standard forms | |
| Dialects | |
| ദേവനാഗരി ലിപി, ഉർദു ലിപി | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Regulated by | കേന്ദ്ര ഹിന്ദി ഡയറക്ടറേറ്റ് (ഹിന്ദി, ഇന്ത്യ),[4] ദേശീയ ഭാഷ അതോറിറ്റി, (ഉർദു, പാകിസ്താൻ); ദേശീയ ഉർദു ഭാഷാ വികസന പരിഷത്ത് (ഉർദു, ഇന്ത്യ)[5] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | hi,ur |
| ISO 639-2 | hin,urd |
| ISO 639-3 | Either:hin – Hindiurd – Urdu |
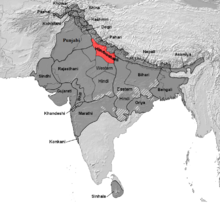 ഹിന്ദുസ്താനി (ഖഡിബോലി/കൗരവി) മാതൃഭാഷയായി സംസാരിക്കുന്ന പ്രദേശങ്ങൾ (ചുവപ്പുനിറം) | |
 ഹിന്ദി അല്ലെങ്കിൽ ഉർദു ഔദ്യോഗിക ഭാഷയായിട്ടുള്ള പ്രദേശങ്ങൾ
സംസ്ഥാന തലം
രണ്ടാം സംസ്ഥാനതലം
ദേശീയ തലം | |
വാമൊഴിയിൽ ഹിന്ദിയും ഉർദുവും തമ്മിൽ വ്യത്യാസങ്ങൾ വളരെ കുറവാണെങ്കിലും ഔദ്യോഗിക വ്യാകരണ നിയമങ്ങൾ തമ്മിൽ സാമ്യം ഏറെയുണ്ടെങ്കിലും സാഹിത്യത്തിലും സാങ്കേതികപദാവലിയിലും ഹിന്ദിയിൽ സംസ്കൃതസ്വാധീനവും ഉർദുവിൽ പേർഷ്യൻ, അറബിക്ക് എന്നിവയുടെ സ്വാധീനവും പ്രകടമാണ്.[11] ഇന്ത്യയുടെ വിഭജനത്തിനു മുമ്പ് ഹിന്ദുസ്താനി, ഹിന്ദി, ഉർദു എന്നിവ ഒരേ ഭാഷയെ സൂചിപ്പിക്കാൻ ഉപയോഗിച്ചിരുന്നു.
ചരിത്രം
തിരുത്തുകമദ്ധ്യകാല ഇന്തോ ആര്യൻ ഭാഷയായ അപഭ്രംശയിൽനിന്നും(अपभ्रंश) 7-ാം നൂറ്റാണ്ടിനും 13-ാം നൂറ്റാണ്ടിനിടക്ക് ഉരുത്തിരിഞ്ഞ ഭാഷയാണ് ഹിന്ദുസ്താനി.[12] ദില്ലിയാണ് ഇതിന്റെ ഈറ്റില്ലം.[13]
ദില്ലി സുൽത്താനത്ത് കാലഘട്ടത്തിൽ അമീർ ഖുസ്രോ ഹിന്ദുസ്താനിയിൽ രചിച്ച കൃതികളിൽ ഹിന്ദവി (ഹിന്ദി: हिन्दवी, ഉർദു: ہندوی) എന്നാണ് ഭാഷയുടെ പേരിനെക്കുറിച്ച് സൂചിപ്പിച്ചിരുന്നത്.
ലിപി
തിരുത്തുകഉർദു പേർഷ്യൻ ലിപിയിൽ
| جھ | ڄ | ج | پ | ث | ٺ | ٽ | ٿ | ت | ڀ | ٻ | ب | ا |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ɟʱ | ʄ | ɟ | p | s | ʈʰ | ʈ | tʰ | t | bʱ | ɓ | b | * |
| ڙ | ر | ذ | ڍ | ڊ | ڏ | ڌ | د | خ | ح | ڇ | چ | ڃ |
| ɽ | r | z | ɖʱ | ɖ | ɗ | dʱ | d | x | h | cʰ | c | ɲ |
| ڪ | ق | ڦ | ف | غ | ع | ظ | ط | ض | ص | ش | س | ز |
| k | x | pʰ | f | ɣ | ∅ | z | t | z | s | ? | s | z |
| ي | ه | و | ڻ | ن | م | ل | ڱ | گھ | ڳ | گ | ک | |
| * | h | * | ɳ | n | m | l | ŋ | ɡʱ | ɠ | ɡ | kʰ |
ഹിന്ദി ദേവനാഗരി ലിപിയിൽ
| अ | आ | इ | ई | उ | ऊ | ए | ऐ | ओ | औ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | ā | i | ī | u | ū | e | ai | o | au |
| क | ख | ख़ | ग | ॻ | ग़ | घ | ङ | ||
| k | kʰ | x | ɡ | ɠ | ɣ | ɡʱ | ŋ | ||
| च | छ | ज | ॼ | ज़ | झ | ञ | |||
| c | cʰ | ɟ | ʄ | z | ɟʱ | ɲ | |||
| ट | ठ | ड | ॾ | ड़ | ढ | ढ़ | ण | ||
| ʈ | ʈʰ | ɖ | ɗ | ɽ | ɖʱ | ɽʱ | ɳ | ||
| त | थ | द | ध | न | |||||
| t | tʰ | d | dʱ | n | |||||
| प | फ | फ़ | ब | ॿ | भ | म | |||
| p | pʰ | f | b | ɓ | bʱ | m | |||
| य | र | ल | व | ||||||
| j | r | l | ʋ | ||||||
| श | ष | स | ह | ||||||
| sh | ʂ | s | h | ||||||
അവലംബം
തിരുത്തുക- ↑ Standard Hindi: 180 million India (1991). Urdu: 48 million India (1997), 11 million Pakistan (1993). Ethnologue 16.
- ↑ 120 million Standard Hindi (1999), 45 million Urdu (1999). Ethnologue 16.
- ↑ BBC: A Guide to Urdu
- ↑ The Central Hindi Directorate regulates the use of Devanagari script and Hindi spelling in India. Source: Central Hindi Directorate: Introduction Archived 2010-04-15 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ National Council for Promotion of Urdu Language
- ↑ Mohammad Tahsin Siddiqi (1994), Hindustani-English code-mixing in modern literary texts, University of Wisconsin,
... Hindustani is the lingua franca of both India and Pakistan ...
- ↑ Lydia Mihelič Pulsipher, Alex Pulsipher, Holly M. Hapke (2005), World Regional Geography: Global Patterns, Local Lives, Macmillan, ISBN 0716719045,
... By the time of British colonialism, Hindustani was the lingua franca of all of northern India and what is today Pakistan ...
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Michael Huxley (editor) (1935), The Geographical magazine, Volume 2, Geographical Press,
... For new terms it can draw at will upon the Persian, Arabic, Turkish and Sanskrit dictionaries ...
{{citation}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ↑ Britain), Royal Society of Arts (Great (1948), Journal of the Royal Society of Arts, Volume 97,
... it would be very unwise to restrict it to a vocabulary mainly dependent upon Sanskrit, or mainly dependent upon Persian. If a language is to be strong and virile it must draw on both sources, just as English has drawn on Latin and Teutonic sources ...
- ↑ Students' Britannica: India: Select essays by Dale Hoiberg, Indu Ramchandani page 175
- ↑ Hindi by Yamuna Kachru
- ↑ Keith Brown, Sarah Ogilvie (2008), Concise Encyclopedia of Languages of the World, Elsevier, ISBN 0080877745,
... Apabhramsha seemed to be in a state of transition from Middle Indo-Aryan to the New Indo-Aryan stage. Some elements of Hindustani appear ... the distinct form of the lingua franca Hindustani appears in the writings of Amir Khusro (1253-1325), who called it Hindwi ...
- ↑ വില്ല്യം ഡാൽറിമ്പിൾ (2006). ദ ലാസ്റ്റ് മുഗൾ - ദ ഫോൾ ഓഫ് എ ഡൈനസ്റ്റി, ഡെൽഹി 1857 (in ഇംഗ്ലീഷ്). പെൻഗ്വിൻ ബുക്സ്. p. 34. ISBN 9780670999255. Retrieved 2013 ജൂലൈ 4.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) ഗൂഗിൾ ബുക്സ് കണ്ണി
ഗ്രന്ഥസൂചിക
തിരുത്തുക- Asher, R. E. (1994). Hindi. In Asher (Ed.) (pp. 1547–1549).
- Asher, R. E. (Ed.). (1994). The Encyclopedia of language and linguistics. Oxford: Pergamon Press. ISBN 0-08-035943-4.
- Bailey, Thomas G. (1950). Teach yourself Hindustani. London: English Universities Press.
- Chatterji, Suniti K. (1960). Indo-Aryan and Hindi (rev. 2nd ed.). Calcutta: Firma K.L. Mukhopadhyay.
- Dua, Hans R. (1992). Hindi-Urdu as a pluricentric language. In M. G. Clyne (Ed.), Pluricentric languages: Differing norms in different nations. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter. ISBN 3-11-012855-1.
- Dua, Hans R. (1994a). Hindustani. In Asher (Ed.) (pp. 1554).
- Dua, Hans R. (1994b). Urdu. In Asher (Ed.) (pp. 4863–4864).
- Rai, Amrit. (1984). A house divided: The origin and development of Hindi-Hindustani. Delhi: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-561643-X.
കൂടുതൽ വായനയ്ക്ക്
തിരുത്തുക- Henry Blochmann (1877). English and Urdu dictionary, romanized (8 ed.). CALCUTTA: Printed at the Baptist mission press for the Calcutta school-book society. p. 215. Retrieved 2011-07-06.the University of Michigan
- John Dowson (1908). A grammar of the Urdū or Hindūstānī language (3 ed.). LONDON: K. Paul, Trench, Trübner & Co., ltd. p. 264. Retrieved 2011-07-06.the University of Michigan
- John Dowson (1872). A grammar of the Urdū or Hindūstānī language. LONDON: Trübner & Co. p. 264. Retrieved 2011-07-06.Oxford University
- John Thompson Platts (1874). A grammar of the Hindūstānī or Urdū language. Vol. Volume 6423 of Harvard College Library preservation microfilm program. LONDON: W.H. Allen. p. 399. Retrieved 2011-07-06.
{{cite book}}:|volume=has extra text (help)Oxford University - John Thompson Platts (1892). A grammar of the Hindūstānī or Urdū language. LONDON: W.H. Allen. p. 399. Retrieved 2011-07-06.the New York Public Library
- John Thompson Platts (1884). A dictionary of Urdū, classical Hindī, and English (reprint ed.). LONDON: H. Milford. p. 1259. Retrieved 2011-07-06.Oxford University
- Shakespear, John. A Dictionary, Hindustani and English. 3rd ed., much enl. London: Printed for the author by J.L. Cox and Son: Sold by Parbury, Allen, & Co., 1834.
- Taylor, Joseph. A dictionary, Hindoostanee and English. Available at Hathi Trust. (A dictionary, Hindoostanee and English / abridged from the quarto edition of Major Joseph Taylor ; as edited by the late W. Hunter ; by William Carmichael Smyth.)
പുറത്തേയ്ക്കുള്ള കണ്ണികൾ
തിരുത്തുക- Hamari Boli (Hindustani) Archived 2013-06-01 at the Wayback Machine.
- Khan Academy (Hindi-Urdu): academic lessons taught in Hindi-Urdu
- Janmaanas Ek Hindi Manch(Hindi Language Forum) Archived 2016-05-03 at the Wayback Machine.
- Encyclopædia Britannica, 11th Edition: Hindostani Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine.
- Hindi, Urdu, Hindustani, khaRî bolî
- Hindustani FAQ
- Hindustani as an anxiety between Hindi–Urdu Commitment
- Hindi? Urdu? Hindustani? Hindi-Urdu? Archived 2006-09-23 at the Wayback Machine.
- History of Hindustani
- Hindi/Urdu-English-Kalasha-Khowar-Nuristani-Pashtu Comparative Word List
- Ethnologue Report for Hindustani
- GRN Report for Hindustani
- Hindustani Poetry Archived 2006-06-15 at the Wayback Machine.
- Hindustani online resources Archived 2006-08-27 at the Wayback Machine.
- Biggest Hindustani-Indian poetry forum
വിക്കിവൊയേജിൽ നിന്നുള്ള ഹിന്ദുസ്താനി ഭാഷ യാത്രാ സഹായി
- National Language Authority (Urdu), Pakistan (muqtadera qaumi zaban) Archived 2007-08-04 at the Wayback Machine.
- The poisonous potency of script: Hindi and Urdu, ROBERT D. KING
| ഭാരതത്തിലെ ഔദ്യോഗിക ഭാഷകൾ |
| ഫെഡറൽതല ഔദ്യോഗിക ഭാഷകൾ |
| ഇംഗ്ലീഷ് • ഹിന്ദി |
| സംസ്ഥാനതല ഔദ്യോഗിക ഭാഷകൾ |
| ആസ്സാമീസ് • ബംഗാളി • ബോഡോ • ദോഗ്രി •ഗോണ്ടി • ഗുജറാത്തി• ഹിന്ദി • കന്നഡ • കശ്മീരി • കൊങ്കണി • മലയാളം • മൈഥിലി • മണിപ്പൂരി • മറാഠി• നേപ്പാളി • ഒറിയ • പഞ്ചാബി • സംസ്കൃതം • സന്താലി • സിന്ധി • തമിഴ് • തെലുങ്ക് • ഉർദു • |