ക്വിനൈൻ
മലേറിയയ്ക്കും ബേബിസിയോസിസിനും ചികിത്സിക്കാൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന ഒരു മരുന്നാണ് ക്വിനൈൻ. [4] ആർട്ടിസ്യൂണേറ്റ് ലഭ്യമല്ലാത്തപ്പോൾ ക്ലോറോക്വിനിനെ പ്രതിരോധിക്കുന്ന പ്ലാസ്മോഡിയം ഫാൽസിപാരം മൂലമുള്ള മലേറിയ ചികിത്സയ്ക്കും ഇതുപയോഗിക്കുന്നു.[5] ചിലപ്പോൾ റെസ്റ്റ്ലെസ് ലെഗ്സ് സിൻഡ്രോം ചികിൽസയിൽ ഉപയോഗിക്കാറുണ്ടെങ്കിലും ഗുരുതരമായ പാർശ്വഫലങ്ങളുടെ അപകടസാധ്യത കാരണം ക്വിനൈൻ ഈ ആവശ്യത്തിനായി ശുപാർശ ചെയ്യുന്നില്ല. ഇത് വായിലൂടെയോ ഇൻട്രാവെനസായോ നൽകാം. ലോകത്തിന്റെ ചില പ്രദേശങ്ങളിൽ ക്വിനൈനിനെ മലേറിയ പ്രതിരോധിക്കുന്നതായി കണ്ടെത്തിയിട്ടുണ്ട്. ടോണിക്ക് വാട്ടറിന്റെ കയ്പേറിയ രുചി നൽകുന്ന ഘടകമാണ് ക്വിനൈൻ. [6][7] സിങ്കോണ മരത്തിന്റെ പുറംതൊലിയിൽ നിന്നാണ് ക്വിനൈൻ വേർതിരിക്കുന്നത്. [4] [8] [9]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | US: /ˈkwaɪnaɪn/, /kwɪˈniːn/ or UK: /ˈkwɪniːn/ KWIN-een |
| Trade names | Qualaquin, Quinate, Quinbisul, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682322 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intramuscular, intravenous, rectal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 70–95%[3] |
| Metabolism | Liver (mostly CYP3A4 and CYP2C19-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 8–14 hours (adults), 6–12 hours (children)[3] |
| Excretion | Kidney (20%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.550 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
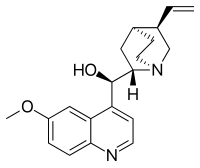
| Formula | C20H24N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 324.42 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 177 °C (351 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |


തലവേദന, ചെവിയിൽ മുഴക്കം അനുഭവപ്പെടുക, കാഴ്ചാപ്രശ്നങ്ങൾ, വിയർക്കൽ എന്നിവയാണ് സാധാരണ പാർശ്വഫലങ്ങൾ. [4] ബധിരത, ത്രോംബോസൈറ്റോപീനിയ, അതാളത എന്നിവയാണ് കൂടുതൽ ഗുരുതരമായ പാർശ്വഫലങ്ങൾ. ഗർഭാവസ്ഥയിൽ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നത് കുഞ്ഞിന് ദോഷം വരുത്തുമോ എന്ന് വ്യക്തമല്ല. ക്വിനൈൻ ഒരു ആൽക്കലോയ്ഡ് ആണ്. ഒരു മരുന്നായി ഇത് എങ്ങനെ പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നുവെന്ന് പൂർണ്ണമായും വ്യക്തമല്ല.
1820-ൽ, സിങ്കോണ മരത്തിന്റെ പുറംതൊലിയിൽ നിന്ന് ക്വിനൈൻ ആദ്യമായി വേർതിരിച്ചു. [4] [10] [11] 1632 മുതൽ മലേറിയ ചികിത്സയ്ക്കായി ഉപയോഗിച്ചിരുന്നു. ജെസ്യൂട്ട് മിഷനറിമാർ 1636 ൽ ഇത് സ്പെയിനിൽ അവതരിപ്പിച്ചു. [12] ലോകാരോഗ്യ സംഘടനയുടെ അവശ്യ മരുന്നുകളുടെ പട്ടികയിലൽപ്പെട്ട ഔഷധമാണിത്.[13]
ഉപയോഗങ്ങൾ
തിരുത്തുക2006 ലെ കണക്കനുസരിച്ച്, മലേറിയയ്ക്കുള്ള ചികിത്സയ്ക്കായി ലോകാരോഗ്യ സംഘടന (ഡബ്ല്യുഎച്ച്ഒ) ക്വിനൈൻ ശുപാർശ ചെയ്യുന്നില്ല, കാരണം പാർശ്വഫലങ്ങൾ കുറവായ, തുല്യമായി ഫലപ്രദമാകുന്ന മറ്റ് വസ്തുക്കളും ഉണ്ട്. ആർടെമിസിനിൻ ലഭ്യമല്ലാത്തപ്പോൾ മാത്രം ഇത് ഉപയോഗിക്കാൻ അവർ ശുപാർശ ചെയ്യുന്നു. [14] [15] [16] [17] ല്യൂപ്പസ്, ആർത്രൈറ്റിസ് എന്നിവയ്ക്കും ക്വിനൈൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു.
ലെഗ് ക്രാംപ് ചികിൽസിക്കാൻ ഒരു ഓഫ്-ലേബൽ ചികിത്സയായി ക്വിനൈൻ പതിവായി നിർദ്ദേശിക്കപ്പെട്ടിരുന്നുവെങ്കിലും, പാർശ്വഫലങ്ങൾ കൂടുതലായതിനാൽ ഇപ്പോൾ, ഇത് സാധാരണയായി ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നില്ല. [18] [19] [20][21]
രസതന്ത്രം
തിരുത്തുകക്വിൻനൈനിന്റെ പ്രായോഗികമായ ഏക ഉറവിടം സിങ്കോണ മരങ്ങളാണ് . എന്നിരുന്നാലും, രണ്ടാം ലോകമഹായുദ്ധസമയത്ത് യുദ്ധകാലത്തെ സമ്മർദ്ദത്തിൽ, അതിന്റെ കൃത്രിമ ഉൽപാദനത്തെക്കുറിച്ചുള്ള ഗവേഷണങ്ങൾ നടന്നു. അമേരിക്കൻ രസതന്ത്രജ്ഞരായ റോബർട്ട് ബി. വുഡ്വാർഡ്, ഡബ്ല്യു.ഇ ഡോറിംഗ് എന്നിവർ 1944 ൽ ഒരു രാസസംയോജനം നടത്തി. [22] [23] പക്ഷേ അവയ്ക്കൊന്നും സ്രോതസ്സുകളിൽ നിന്നും ആൽക്കലോയിഡിനെ വേർതിരിക്കുന്നതിൽ, സാമ്പത്തികമായി മത്സരിക്കാൻ കഴിഞ്ഞില്ല.
1
അവലംബം
തിരുത്തുക- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Quinine Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 25 March 2020. Retrieved 13 August 2020.
- ↑ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Qualaquin (quinine) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Archived from the original on 2 February 2014. Retrieved 29 January 2014.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "Quinine sulfate". Drugs.com. 2020-02-20. Retrieved 2020-05-14.
- ↑ "Artemether for severe malaria". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 6: CD010678. June 2019. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010678.pub3. PMC 6580442. PMID 31210357.
- ↑ Olmsted, John; Williams, Gregory M. (1997). Chemistry: The Molecular Science. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 137. ISBN 978-0-815-18450-8. Archived from the original on 15 September 2016.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ↑ Charming, Cheryl (2006). Miss Charming's Guide for Hip Bartenders and Wayout Wannabes. USA: Sourcebooks, Inc. p. 189. ISBN 978-1-4022-0804-1.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ↑ Willcox, Merlin (28 June 2004). Traditional Medicinal Plants and Malaria. CRC Press. p. 231. ISBN 9780203502327.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ↑ Cechinel-Filho, Valdir (2012). Plant bioactives and drug discovery : principles, practice, and perspectives. Hoboken, N.J.: John Wiley & Sons. p. 2. ISBN 9780470582268. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ↑ Willcox, Merlin (28 June 2004). Traditional Medicinal Plants and Malaria. CRC Press. p. 231. ISBN 9780203502327.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ↑ Cechinel-Filho, Valdir (2012). Plant bioactives and drug discovery : principles, practice, and perspectives. Hoboken, N.J.: John Wiley & Sons. p. 2. ISBN 9780470582268. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ↑ Staines, Henry M.; Krishna, Sanjeev (2011). Treatment and Prevention of Malaria : Antimalarial Drug Chemistry, Action and Use. [S.l.]: Springer Verlag. p. 45. ISBN 9783034604796.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ↑ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2006). "Guidelines for the treatment of malaria" (PDF). World Health Organization. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 August 2009. Retrieved 10 August 2009.
- ↑ "Artesunate versus quinine for treatment of severe falciparum malaria: a randomised trial". Lancet. 366 (9487): 717–25. 2005. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67176-0. PMID 16125588.
- ↑ "Oral quinine for the treatment of uncomplicated malaria" (PDF). BMJ. 339: b2066. July 2009. doi:10.1136/bmj.b2066. PMID 19622550.
- ↑ "Effectiveness of quinine versus artemether-lumefantrine for treating uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Ugandan children: randomised trial". BMJ. 339: b2763. July 2009. doi:10.1136/bmj.b2763. PMC 2714631. PMID 19622553.
- ↑ "FDA Drug Safety Communication: New risk management plan and patient Medication Guide for Qualaquin (quinine sulfate)". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 2010-08-07. Archived from the original on 19 February 2011. Retrieved 2011-02-21.
- ↑ "Serious risks associated with using Quinine to prevent or treat nocturnal leg cramps (September 2012)". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 2012-08-31. Archived from the original on 22 October 2016. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "Quinine for Night-Time Leg Cramps". Consumer Reports. Retrieved 2020-01-20.
- ↑ Lowe, Derek (22 January 2019). "Quinine's Target". Science. Archived from the original on 2019-01-29. Retrieved 28 January 2019.
- ↑ "The Total Synthesis of Quinine". J Am Chem Soc. 66 (849): 849. 1944. doi:10.1021/ja01233a516.
- ↑ Kaufman, Teodoro S.; Rúveda, Edmundo A. (2005). "Die Jagd auf Chinin: Etappenerfolge und Gesamtsiege". Angewandte Chemie International Edition (in ജർമ്മൻ). 117 (6): 876–907. doi:10.1002/ange.200400663.