ഓക്സാലിക് ആസിഡ്
രാസസംയുക്തം
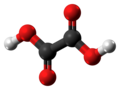
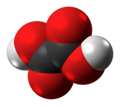
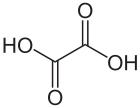
C2H2O4 ഫോർമുലയോടുകൂടിയ ഒരു ഓർഗാനിക് സംയുക്തമാണ് ഓക്സാലിക് ആസിഡ്. വർണ്ണരഹിതമായ പരൽ രൂപത്തിലുള്ള പദാർത്ഥമായ ഓക്സാലിക് ആസിഡ് ജലത്തിൽ നിറമില്ലാത്ത ഒരു ലായനിയാണ്. HooCCOOH ആണ് ഇതിന്റെ ഘടന, ഡൈകാർബോക്സിലിക് ആസിഡായ ഈ ആസിഡ് അസെറ്റിക് ആസിഡിനേക്കാൾ അമ്ലവീര്യം വളരെ കൂടുതലാണ്. ഓക്സാലിക് ആസിഡ് ഒരു നിരോക്സീകാരിയാണ്. [8]ഇതിന്റെ സംയുഗ്മകക്ഷാരം (conjugate base) ഓക്സലേറ്റ് (C
2O2−
4) എന്നറിയപ്പെടുന്നു.
| |||
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Oxalic acid[1] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Ethanedioic acid[1] | |||
| Other names
Wood bleach
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| Beilstein Reference | 385686 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.123 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| Gmelin Reference | 2208 | ||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | {{{value}}} | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 3261 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| InChI | |||
| SMILES | |||
| Properties | |||
| തന്മാത്രാ വാക്യം | |||
| Molar mass | 0 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White crystals | ||
| Odor | odorless | ||
| സാന്ദ്രത | 1.90 g cm−3 (anhydrous, at 17 °C)[2] 1.653 g cm−3 (dihydrate) | ||
| ദ്രവണാങ്കം | |||
| 90-100 g/L (20 °C)[2] | |||
| Solubility | 237 g/L (15 °C) in ethanol 14 g/L (15 °C) in diethyl ether [3] | ||
| ബാഷ്പമർദ്ദം | <0.001 mmHg (20 °C)[4] | ||
| അമ്ലത്വം (pKa) | 1.25, 4.14[5] | ||
| Conjugate base | Hydrogenoxalate | ||
| -60.05·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | corrosive | ||
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS | ||
| Flash point | {{{value}}} | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LDLo (lowest published)
|
1000 mg/kg (dog, oral) 1400 mg/kg (rat) 7500 mg/kg (rat, oral)[7] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3[6] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 ST 2 mg/m3[6] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
500 mg/m3[6] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
അവലംബം
തിരുത്തുക- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. pp. P001 – P004. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ↑ Radiant Agro Chem. "Oxalic Acid MSDS". Archived from the original on 2011-07-15. Retrieved 2019-01-05.
- ↑ Wood-Black, Frankie (2000-03). "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards and Other Databases DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 99-115". Chemical Health and Safety. 7 (2): 52. doi:10.1016/s1074-9098(99)00094-5. ISSN 1074-9098.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ Bjerrum, J., et al. (1958) Stability Constants, Chemical Society, London.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0474". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ "Oxalic acid". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley. 2005. pp. 17624/28029. doi:10.1002/14356007. ISBN 9783527306732.
പുറം കണ്ണികൾ
തിരുത്തുകWikimedia Commons has media related to Oxalic acid.
- Oxalic acid MS Spectrum
- International Chemical Safety Card 0529
- NIOSH Guide to Chemical Hazards (CDC)
- Table: Oxalic acid content of selected vegetables (USDA)
- Alternative link: Table: Oxalic Acid Content of Selected Vegetables (USDA)
- About rhubarb poisoning (The Rhubarb Compendium) Archived 2008-10-16 at the Wayback Machine.
- Oxalosis & Hyperoxaluria Foundation (OHF) The Oxalate Content of Food 2008 (PDF)
- Oxalosis & Hyperoxaluria Foundation (OHF) Diet Information
- Calculator: Water and solute activities in aqueous oxalic acid Archived 2009-05-11 at the Wayback Machine.