യൂട്ടെറിൻ ഇൻവേർഷൻ
സാധാരണയായി പ്രസവത്തെ പിന്തുടർന്ന് ഗർഭപാത്രം അകത്തേക്ക് തിരിയുന്നതാണ് യൂട്ടെറിൻ ഇൻവേർഷൻ.[1] പ്രസവാനന്തര രക്തസ്രാവം, വയറുവേദന, യോനിയിലെ പിണ്ഡം, കുറഞ്ഞ രക്തസമ്മർദ്ദം എന്നിവ ലക്ഷണങ്ങളാണ്. [1] അപൂർവ്വമായി യൂട്ടെറിൻ ഇൻവേർഷൻ ഗർഭധാരണവുമായി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ട് സംഭവിക്കുന്നില്ല. [5]
| യൂട്ടെറിൻ ഇൻവേർഷൻ | |
|---|---|
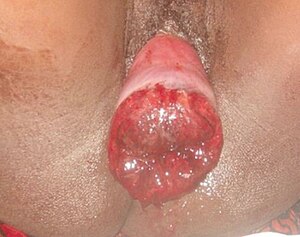 | |
| Complete inverted uterus | |
| സ്പെഷ്യാലിറ്റി | Obstetrics |
| ലക്ഷണങ്ങൾ | Postpartum bleeding, abdominal pain, mass in the vagina, low blood pressure[1] |
| തരങ്ങൾ | First, second, third, fourth degree[1] |
| അപകടസാധ്യത ഘടകങ്ങൾ | Pulling on the umbilical cord or pushing on the top of the uterus before the placenta has detached, uterine atony, placenta previa, connective tissue disorders[1] |
| ഡയഗ്നോസ്റ്റിക് രീതി | Seeing the inside of the uterus in the vagina[2] |
| ഡിഫറൻഷ്യൽ ഡയഗ്നോസിസ് | Uterine fibroid, uterine atony, bleeding disorder, retained placenta[1] |
| Treatment | Standard resuscitation, rapidly replacing the uterus[1] |
| മരുന്ന് | Oxytocin, antibiotics[1] |
| രോഗനിദാനം | ~15% risk of death[3] |
| ആവൃത്തി | About 1 in 6,000 deliveries[1][4] |
മറുപിള്ള വേർപെടുത്തുന്നതിനുമുമ്പ് പൊക്കിൾക്കൊടി വലിച്ചെടുക്കുന്നതിനോ ഗർഭപാത്രത്തിന്റെ മുകളിൽ തള്ളുന്നതോ അപകടസാധ്യത ഘടകങ്ങളിൽ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നു. [1]മറ്റ് അപകടസാധ്യത ഘടകങ്ങൾ ഗർഭപാത്രത്തിന്റെ ഉള്ളിൽ ഒന്നുകിൽ അല്ലെങ്കിൽ പുറത്തുവരുന്നതാണ് രോഗനിർണയം. [2][6]
10,000 ഡെലിവറികളിൽ 1 വീതവും 2,000 മുതൽ 1 വീതവും യൂട്ടെറിൻ ഇൻവേർഷൻ സംഭവിക്കുന്നു. വികസ്വര രാജ്യങ്ങളിൽ നിരക്കുകൾ കൂടുതലാണ്. [1][4] അമ്മയുടെ മരണ സാധ്യത 15% ആണ്, ചരിത്രപരമായി ഇത് 80% വരെ ഉയർന്നതാണ്. [3][1]300 ബിസി മുതൽ ഹിപ്പോക്രാറ്റസ് ഈ അവസ്ഥ വിവരിച്ചിരിക്കുന്നു. [1]
അടയാളങ്ങളും ലക്ഷണങ്ങളും
തിരുത്തുകയൂട്ടെറിൻ ഇൻവേർഷൻ പലപ്പോഴും കാര്യമായ പ്രസവാനന്തര രക്തസ്രാവവുമായി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ടിരിക്കുന്നു. പരമ്പരാഗതമായി, രക്തദാനസമയത്ത് ഹമെമോഡൈനാമിക് ഷോക്ക് ആനുപാതികമായി "അവതരിപ്പിച്ചതായി കരുതപ്പെട്ടിരുന്നു, എന്നിരുന്നാലും രക്ത നഷ്ടം പലപ്പോഴും കുറച്ചുകാണുന്നു. ഗർഭാശയ ലിഗമെന്റ്സിലെ പാരാസിമ്പതെറ്റിക് പ്രഭാവം ബ്രാഡികാർഡിയയ്ക്ക് കാരണമായേക്കാം.
എപ്പിഡെമിയോളജി
തിരുത്തുക10,000 ഡെലിവറികളിൽ 1 വീതവും 2,000 മുതൽ 1 വീതവും യൂട്ടെറിൻ ഇൻവേർഷൻ സംഭവിക്കുന്നു.[1][4]വികസ്വര രാജ്യങ്ങളിൽ ഇതിന്റെ നിരക്കുകൾ കൂടുതലാണ്.[1]
അവലംബം
തിരുത്തുക- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 Bhalla, Rita; Wuntakal, Rekha; Odejinmi, Funlayo; Khan, Rehan U (January 2009). "Acute inversion of the uterus". The Obstetrician & Gynaecologist. 11 (1): 13–18. doi:10.1576/toag.11.1.13.27463.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Mirza, FG; Gaddipati, S (April 2009). "Obstetric emergencies". Seminars in Perinatology. 33 (2): 97–103. doi:10.1053/j.semperi.2009.01.003. PMID 19324238.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Gandhi, Alpesh; Malhotra, Narendra; Malhotra, Jaideep; Gupta, Nidhi; Bora, Neharika Malhotra (2016). Principles of Critical Care in Obstetrics (in ഇംഗ്ലീഷ്). Springer. p. 335. ISBN 9788132226925.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Andersen, H. Frank; Hopkins, Michael P. (2009). "Postpartum Hemorrhage". The Global Library of Women's Medicine. doi:10.3843/GLOWM.10138.
- ↑ Mehra, R; Siwatch, S; Arora, S; Kundu, R (12 December 2013). "Non-puerperal uterine inversion caused by malignant mixed mullerian sarcoma". BMJ Case Reports. 2013: bcr2013200578. doi:10.1136/bcr-2013-200578. PMC 3863018. PMID 24334469.
- ↑ Apuzzio, Joseph J.; Vintzileos, Anthony M.; Berghella, Vincenzo; Alvarez-Perez, Jesus R. (2017). Operative Obstetrics, 4E (in ഇംഗ്ലീഷ്). CRC Press. p. PT822. ISBN 9781498720588.