കവര്
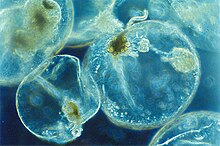
നൊക്റ്റിലൂക്ക സിന്റിലൻസ് എന്ന സ്വതന്ത്രമായി ജീവിക്കുന്ന ഡൈനോഫ്ലജെല്ലേറ്റ് സമുദ്രജീവിയുടെ ജൈവ ദീപ്തിയാണ് കവര് (sea sparkle). [1] [2] ഇവ ലോകത്തെമ്പാടും തീരത്തോടടുത്തുള്ള പ്രദേശങ്ങളിൽ കാണപ്പെടുന്നു. ഒരു ഏകകോശ പ്രോട്ടിസ്റ്റ ആയ ഈ ജീവിയുടെ സിന്റിലോണുകൾ എന്നറിയപ്പെടുന്ന ഗോളാകൃതിയിലുള്ള ആയിരക്കണക്കിന് കോശാംഗങ്ങളിൽ നടക്കുന്ന ല്യൂസിഫെറിൻ-ല്യൂസിഫെറേസ് പ്രവർത്തനത്തിന്റെ ഫലമായി അതിന്റെ കോശദ്രവ്യത്തിൽ ആകമാനം ജൈവദീപ്തി ഉല്പാദിപ്പിക്കപ്പെടുന്നു.
| Noctiluca scintillans | |
|---|---|
| |
| ശാസ്ത്രീയ വർഗ്ഗീകരണം | |
| Domain: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Noctiluca
|
| Species: | N. scintillans
|
| Binomial name | |
| Noctiluca scintillans (Macartney) Kofoid & Swezy, 1921 | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Noctiluca miliaris | |
നൊക്റ്റിലൂക്ക സിന്റിലൻസ് പ്ലാങ്ക്ടൻ, ഡയാറ്റമുകൾ, മറ്റ് ഡൈനൊഫ്ലജെല്ലേറ്റുകൾ, മത്സ്യങ്ങളുടെ മുട്ട, ബാക്റ്റീരിയ എന്നിവയെ ഫാഗോസൈറ്റോസിസ് വഴി വിഴുങ്ങുന്നു.[3] ഇവയുടെ ഭക്ഷണമായ ഫൈറ്റോ പ്ലാങ്ക്റ്റണുകൾ ധാരാളമുള്ള പ്രദേശങ്ങളിൽ നൊക്റ്റിലൂക്ക സിന്റിലൻസ് കൂടുതലായി കാണപ്പെടാറുണ്ട്. പോഷകസമൃദ്ധമായ വെള്ളവും അനുകൂലമായ കാലാവസ്ഥയും ഇവ കൂടുതൽ കാണുന്നതിന് അനുകൂലമായ സാഹചര്യങ്ങളാണ്. വെള്ളത്തിന് ഇളക്കം ഉണ്ടാകുമ്പോൾ നൊക്റ്റിലൂക്ക സിന്റിലൻസ് ഉണ്ടാക്കുന്ന തിളക്കം വെള്ളത്തിനു മുകളിൽ ദീപ്തിയായി കാണാം.[4]
ഇതും കാണുക
തിരുത്തുകഅവലംബങ്ങൾ
തിരുത്തുക- ↑ "Image of the "Sea Sparkle" from 'Britannica Online Encyclopedia'". Britannica.com. Retrieved 2013-09-13.
- ↑ https://www.thenewsminute.com/article/magical-glow-sea-kumbalangi-nights-secret-behind-sparkle-96887
- ↑ https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/pbr/1/2/1_2_97/_article
- ↑ https://www.irishtimes.com/news/lights-in-irish-sea-are-natural-1.847896
കൂടുതൽ വായനയ്ക്ക്
തിരുത്തുക- Eckert R, Reynolds GT (1967). "The subcellular origin of bioluminescence in Noctiluca miliaris". J. Gen. Physiol. 50 (5): 1429–58. doi:10.1085/jgp.50.5.1429. PMC 2225713. PMID 5340466.
- Elbrächter, M.; Qi, Y.Z. (1998). "Aspects of Noctiluca (Dinophyceae) population dynamics". In Anderson, Donald Mark; Cembella, Allan D.; Hallegraeff, Gustaaf M. (eds.). Physiological Ecology of Harmful Algal Blooms. NATO ASI series: Ecological sciences. Vol. 41. Springer. pp. 315–335. ISBN 978-3-540-64117-9.
- Hausmann, Klaus; Hülsmann, N.; Radek, Renate (2003). Protistology (3rd ed.). E. Schweizerbart'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung. ISBN 978-3-510-65208-2.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Lenaers G, Scholin C, Bhaud Y, Saint-Hilaire D, Herzog M (1991). "A molecular phylogeny of dinoflagellate protists (pyrrhophyta) inferred from the sequence of 24S rRNA divergent domains D1 and D8". J. Mol. Evol. 32 (1): 53–63. doi:10.1007/BF02099929. PMID 1901368.
- Murray S, Flø Jørgensen M, Ho SY, Patterson DJ, Jermiin LS (2005). "Improving the analysis of dinoflagellate phylogeny based on rDNA". Protist. 156 (3): 269–86. doi:10.1016/j.protis.2005.05.003. PMID 16325541.
- Palmer, Jefferey D. (2003). "The Symbiotic Birth and Spread of Plastids: How Many Times and Whodunit?". J. Phycol. 39: 4–11. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8817.2003.02185.x.
- Tada, Kuninao; Pithakpol, Santiwat; Yano, Rumiko; Montani, Shigeru (2000). "Carbon and nitrogen content of Noctiluca scintillans in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan". Journal of Plankton Research. 22 (6): 1203–11. doi:10.1093/plankt/22.6.1203.
- Kiørboe, Thomas; Titelman, Josefin (1998). "Feeding, prey selection and prey encounter mechanisms in the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans". Journal of Plankton Research. 20 (8): 1615–36. doi:10.1093/plankt/20.8.1615.
- Umani, S. Fonda; Beran, A.; Parlato, S.; Virgilio, D.; Zollet, T.; De Olazabal, A.; Lazzarini, B.; Cabrini, M. (2004). "Noctiluca scintillans MACARTNEY in the Northern Adriatic Sea: long-term dynamics, relationships with temperature and eutrophication, and role in the food web". Journal of Plankton Research. 26 (5): 545–561. doi:10.1093/plankt/fbh045.
പുറത്തേക്കുള്ള കണ്ണികൾ
തിരുത്തുക- "Noctiluca scintillans". Guide to the Marine Zooplankton of south eastern Australia. Tasmanian Aquaculture & Fisheries Institute. 2011-11-30.