ലാക്രിമൽ സാക്ക്
ലാക്രിമൽ സിസ്റ്റത്തിൽ, ലാക്രിമൽ ഡക്റ്റിന്റെ മുകൾവശത്തുള്ള സഞ്ചി പോലെ തോന്നിക്കുന്ന ഭാഗമാണ് ലാക്രിമൽ സഞ്ചി അല്ലെങ്കിൽ ലാക്രിമൽ സാക്ക് എന്ന് അറിയപ്പെടുന്നത്.[1] ഇത് ലാക്രിമൽ അസ്ഥിയും മാക്സില്ലയുടെ ഫ്രോണ്ടൽ പ്രോസസും ചേർന്ന് രൂപംകൊള്ളുന്ന കുഴി പോലുള്ള ഭാഗത്ത് സ്ഥിതി ചെയ്യുന്നു. ഇത് കണ്ണിന്റെ ഉപരിതലത്തിൽ നിന്നുള്ള കണ്ണുനീർ വഹിക്കന്ന ലാക്രിമൽ കനാലികുലൈയെയും ഈ ദ്രാവകം നാസികാദ്വാരത്തിലേക്ക് എത്തിക്കുന്ന നാസോലാക്രിമൽ നാളത്തെയും ബന്ധിപ്പിക്കുന്നു. [2] ലാക്രിമൽ സഞ്ചി അടയുന്നത് ഡാക്രിയോസിസ്റ്റൈറ്റിസിലേക്ക് നയിക്കുന്നു.[3]
| ലാക്രിമൽ സാക്ക് | |
|---|---|
 The lacrimal apparatusis shown through dissection on the left side. | |
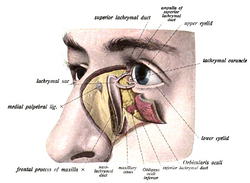 The lacrimal sac has been opened showing internal organization as well as the naso-lacrymal duct. | |
| Details | |
| Artery | angular artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | saccus lacrimalis |
| TA | A15.2.07.068 |
| FMA | 20289 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
ഘടന
തിരുത്തുകഓവൽ രൂപത്തിലുള്ള ഇതിന് 12 മുതൽ 15 മില്ലീമീറ്റർ വരെ നീളമുണ്ട്; അതിന്റെ അടഞ്ഞ മുകൾഭാഗം വൃത്താകൃതിയിലാണ്; താഴത്തെ ഭാഗം നാസോലാക്രിമൽ നാളത്തിലേക്ക് തുടരുന്നു.
അതിന്റെ പുറം ഉപരിതലം മീഡിയൽ പാൽപെബ്രൽ ലിഗമെന്റിൽ നിന്ന് ഉരുത്തിരിഞ്ഞ ഒരു നാരുകളുള്ള ഘടനയാൽ മൂടുന്നു, അതിന്റെ ആഴത്തിലുള്ള ഉപരിതലത്തെ ഓർബിക്യുലാരിസ് ഒക്കുലൈ പേശിയുടെ ലാക്രിമൽ ഭാഗം മറികടക്കുന്നു, ഇത് ലാക്രിമൽ അസ്ഥിയിലെ ക്രസ്റ്റിൽ ഘടിപ്പിച്ചിരിക്കുന്നു.
ഹിസ്റ്റോളജി
തിരുത്തുകനാസോലാക്രിമൽ നാളം പോലെ, മ്യൂക്കസ്-സ്രവിക്കുന്ന ഗോബ്ലറ്റ് സെല്ലുകൾ, ചുറ്റുമുള്ള കണക്റ്റീവ് ടിഷ്യുകൾ എന്നിവയുള്ള സ്ട്രാറ്റേറ്റഡ് കോളംനാർ എപിത്തീലിയം എന്നിവയാൽ സഞ്ചി പൊതിയുന്നു. ലാക്രിമൽ സാക്കിലൂടെ കടന്നു പോകുന്ന, കണ്ണിൽ നിന്നും പൊടി അവശിഷ്ടങ്ങളും സൂക്ഷ്മാണുക്കളും നീക്കം ചെയ്യുന്നു.
പ്രവർത്തനം
തിരുത്തുകകണ്ണിൽ നിന്നും ലാക്രിമൽ ഡക്റ്റിലേക്ക് ഒഴുകുന്ന കണ്ണുനീർ ശേഖരിക്കപ്പെടുന്ന ഒരു റിസർവോയറായി ഇത് പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നു.
ഇമേജിംഗ്
തിരുത്തുകലാക്രിമൽ സാക്ക്, റേഡിയോകോൺട്രാസ്റ്റ് കുത്തിവയ്ക്കുകയും തുടർന്ന് എക്സ്-റേ ഇമേജിംഗ് നടത്തുകയും ചെയ്യുന്ന ഡാക്രോസിസ്റ്റോഗ്രാഫി ഉപയോഗിച്ച് ചിത്രീകരിക്കാൻ കഴിയും.
അധിക ചിത്രങ്ങൾ
തിരുത്തുക-
ഇടത് ഓർബിറ്റിൻ്റെ മീഡിയൽ വാൾ
-
ഇടത് ഓർബിക്യുലാരിസ് ഒക്കുലി, പിന്നിൽ നിന്നുള്ള കാഴ്ച
-
ലാക്രിമൽ അപ്പാരറ്റസ് . വലത് വശം. (മുകളിൽ വലതുവശത്ത് ലാക്രിമൽ സഞ്ചി ദൃശ്യമാണ്.)
-
ടാർസിയും അവയുടെ അസ്ഥിബന്ധങ്ങളും. വലത് കണ്ണ്; മുൻ കാഴ്ച. (മധ്യ വലതുഭാഗത്ത് ലാക്രിമൽ സഞ്ചി ദൃശ്യമാണ്.)
ഇതും കാണുക
തിരുത്തുകഅവലംബം
തിരുത്തുക- ↑ Sacks, Raymond; Naidoo, Yuresh (2019-01-01). Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy. pp. 143–148.e1. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-47664-5.00017-1. ISBN 9780323476645. Retrieved 2020-05-08.
Anatomy: The lacrimal sac extends approximately 10 mm above the axilla of the middle turbinate.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ↑ Remington, Lee Ann (2012). "Ocular Adnexa and Lacrimal System". Clinical Anatomy and Physiology of the Visual System. Elsevier. pp. 159–181. doi:10.1016/b978-1-4377-1926-0.10009-8. ISBN 978-1-4377-1926-0.
The lacrimal sac lies within a fossa in the anterior portion of the medial orbital wall. This fossa is formed by the frontal process of the maxillary bone and the lacrimal bone. The sac is surrounded by fascia, continuous with the periorbita, which runs from the anterior to the posterior lacrimal crests.
- ↑ Beare, Nicholas A.V.; Bastawrous, Andrew (2014). "Ophthalmology in the Tropics and Sub-tropics". Manson's Tropical Infectious Diseases. Elsevier. pp. 952–994.e1. doi:10.1016/b978-0-7020-5101-2.00068-6. ISBN 978-0-7020-5101-2.
Tears drain through the canaliculi, lacrimal sac and naso-lacrimal duct into the nose. Blockage of the naso-lacrimal duct prevents drainage of the lacrimal sac, which may lead to infection, causing a painful swelling at the side of the nose below the medial canthus. This may present as a chronically watery, discharging eye, or as an acutely inflamed abscess. This should be treated with oral broad-spectrum antibiotics. The problem may recur unless drainage into the nose is re-established.
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.