ഹൃദയസ്തംഭനം
ഹൃദയ സ്തംഭനം, ഹൃദയാഘാതം എന്നീ പദങ്ങൾ മലയാള ഭാഷയിൽ വിവേചനമില്ലാതെ ഉപയോഗിക്കാറുണ്ട്. എന്നാൽ വൈദ്യ ശാസ്ത്ര നിർവച്ചനത്തിൽ ഇവ രണ്ട് വ്യത്യസ്തങ്ങളായ രോഗാവസ്ഥകളാണ്.
| Cardiac arrest | |
|---|---|
| മറ്റ് പേരുകൾ | Cardiopulmonary arrest, circulatory arrest, sudden cardiac arrest (SCA), sudden cardiac death (SCD)[1][1] |
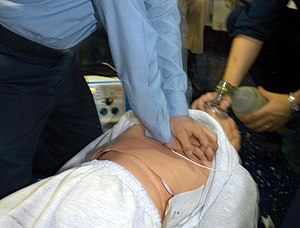 | |
| CPR being administered during a simulation of cardiac arrest. | |
| സ്പെഷ്യാലിറ്റി | Cardiology, emergency medicine |
| ലക്ഷണങ്ങൾ | Loss of consciousness, abnormal or no breathing[1][2] |
| സാധാരണ തുടക്കം | Older age[3][3] |
| കാരണങ്ങൾ | Coronary artery disease, congenital heart defect, major blood loss, lack of oxygen, very low potassium, heart failure[4] |
| ഡയഗ്നോസ്റ്റിക് രീതി | Finding no pulse[1] |
| പ്രതിരോധം | Not smoking, physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, healthy eating[5] |
| Treatment | Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), defibrillation[6] |
| രോഗനിദാനം | Survival rate ~ 10% (outside of hospital) 25% (in hospital)[7][8] |
| ആവൃത്തി | 13 per 10,000 people per year (outside hospital in the US) |
| മരണം | > 425,000 per year (U.S.)[9] |
ഹൃദയാഘാതം Heart Attack , മലയാളികൾ “അറ്റാക്ക്’’ എന്ന് മാത്രമായി ചുരുക്കുന്നു. സാങ്കേതികമായി Myocardial Infarction എന്നാണ് പറയുക. ഹൃദയപേശികളെ ഹനിക്കും വിധം അവയിലേക്കുള്ള രക്തത്തിന്റെ ഒഴുക്ക തടസ്സപ്പെടുന്നതാണ് അറ്റാക്ക് അഥവ myocardial infarction. ഹൃദയത്തിലേക്കുള്ള ഒഴുക്കിനു ഭംഗം സംഭവിക്കുന്നതാണ് കാരണം.
ഹൃദയസ്തംഭനം - cardiac Arrest എന്നതിനു അനുയോജ്യമായ മലയാള പദം.
ഹാർട്ട് അറ്റാക്കിൽ നിന്നും വ്യത്യസ്തമായി ഇവിടെ ഹൃദയമിടിപ്പിലെ തകരാറുകൾ മൂലം ഹൃദയം കാര്യക്ഷമ മായി രക്തം പമ്പ് ചെയ്യാതാവുകയും അത് മൂലം ഓക്സീകരണം നടന്ന രക്ണ്ത്തിന്റെ ലഭ്യത്ക്കുറവ്വ് അനുഭവപെടുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.ഹൃദയത്തിൽ നിന്നുമുള്ള ഒഴുക്കിനാണ് ഇവിടെ തകരാറ് സംഭവിക്കുന്നത്.[5][6]
ലക്ഷണങ്ങൾ
തിരുത്തുകബോധക്ഷയം, ക്ഷീണം,തലചുറ്റൽ , നെഞ്ച് വേദന, കിതപ്പ് , ബലക്ഷയം, ഛർദ്ദി, എന്നിവയിൽ ചിലത് അറസ്റ്റിനു മുന്നോടിയായി പ്രകടമായേക്കാം. എന്നാൽ ഇവയിൽ ഒന്നു പോലുമില്ലാതെ പൊടുന്നനേയും ഹൃദയസ്തംഭനം സംജാതമാവാം.
ഹൃദയസ്തംഭനം സംഭവിച്ചാൽ നാഡിമിടിപ്പ് നിലയ്ക്കലാണ് ഏറ്റവും പ്രകടമായ കണ്ടെത്തൽ. ഹൃദയമിടിപ്പിന്റ് പ്രതിഫലമാണ് നാഡിമിടിപ്പ് എന്നതിനാൽ നാഡിമിടിപ്പ് നിർണ്ണയിക്കാൻ സാധിക്കാതാവുന്നു. ഉടനടി ചികിൽസാമുറകളോ, ജീവൻ രക്ഷാ നടപടികളോ ആരംഭിച്ചില്ലെങ്കിൽ മരണം, സുനിശ്ചിതമാണ്.
കാരണങ്ങൾ
തിരുത്തുകഹൃദയസ്തംഭനത്തിലേക്ക് നയിക്കുന്ന കാരണങ്ങൾ നിരവധിയുണ്ട്. ഇതിൽ ഏറ്റവും പ്രധാനവും ഹൃദയ ധമനീ രോഗമാണ് (Coronary Artery Disease, Coronary Heart Disease CAD/CHD). ഇത് മൂലം രക്ത ഒഴുക്ക് താളം തെറ്റുകയും, ഹൃദയത്തിന്റെ വിദ്യുത് പ്രവർത്തനം അവതാളത്തിലാവുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു. ഹൃദയതാള വൈകല്യങ്ങൾ (fibrillations) ഉണ്ടാവുന്നു. അറവീക്കം (ventricular hypertrophy) സംഭവിക്കുന്ന അവസ്ഥയിൽ മരണ നിരക്ക് ഏറെയാണ്. ദീർഘകാലമായി നിലനിൽക്കുന്ന രക്താതിമർദ്ദം (longstanding Hypertension), ഈ അവസ്ഥകളിലേക്ക് എത്തിക്കുന്നതിൽ നിർണ്ണായകമാണ്.[4][7][10][2]
ധമനീ രോഗം അല്ലാതെയുള്ള കാരണങ്ങളിൽ ചിലത്;
കായിക അധ്വാനമോ, ശരീര സമ്മർദ്ദങ്ങളൊ- Physical Stress.
മഗ്നീഷ്യം, പൊട്ടാഷിയം എന്നീ ധാതുക്കളുടെ കുറവ്.
അമിത രക്തസ്രാവം
ഹൃദയപേശീ രോഗങ്ങൾ-cardiomyopathy
അവലംബം
തിരുത്തുക- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Field JM (2009). The Textbook of Emergency Cardiovascular Care and CPR (in ഇംഗ്ലീഷ്). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 11. ISBN 9780781788991. Archived from the original on 2017-09-05.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Sudden Cardiac Arrest?". NHLBI. June 22, 2016. Archived from the original on 27 August 2016. Retrieved 16 August 2016.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Who Is at Risk for Sudden Cardiac Arrest?". NHLBI. June 22, 2016. Archived from the original on 23 August 2016. Retrieved 16 August 2016.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "What Causes Sudden Cardiac Arrest?". NHLBI. June 22, 2016. Archived from the original on 28 July 2016. Retrieved 16 August 2016.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "How Can Death Due to Sudden Cardiac Arrest Be Prevented?". NHLBI. June 22, 2016. Archived from the original on 27 August 2016. Retrieved 16 August 2016.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "How Is Sudden Cardiac Arrest Treated?". NHLBI. June 22, 2016. Archived from the original on 27 August 2016. Retrieved 16 August 2016.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Adams JG (2012). Emergency Medicine: Clinical Essentials (Expert Consult – Online) (in ഇംഗ്ലീഷ്). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1771. ISBN 978-1455733941. Archived from the original on 2017-09-05.
- ↑ Andersen, LW; Holmberg, MJ; Berg, KM; Donnino, MW; Granfeldt, A (26 March 2019). "In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A Review". JAMA. 321 (12): 1200–1210. doi:10.1001/jama.2019.1696. PMC 6482460. PMID 30912843.
- ↑ Meaney, PA; Bobrow, BJ; Mancini, ME; Christenson, J; de Caen, AR; Bhanji, F; Abella, BS; Kleinman, ME; Edelson, DP; Berg, RA; Aufderheide, TP; Menon, V; Leary, M; CPR Quality Summit Investigators, the American Heart Association Emergency Cardiovascular Care Committee, and the Council on Cardiopulmonary, Critical Care, Perioperative and, Resuscitation. (23 July 2013). "Cardiopulmonary resuscitation quality: [corrected] improving cardiac resuscitation outcomes both inside and outside the hospital: a consensus statement from the American Heart Association". Circulation. 128 (4): 417–35. doi:10.1161/CIR.0b013e31829d8654. PMID 23801105.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Kronick SL, Kurz MC, Lin S, Edelson DP, Berg RA, Billi JE, Cabanas JG, Cone DC, Diercks DB, Foster JJ, Meeks RA, Travers AH, Welsford M (November 2015). "Part 4: Systems of Care and Continuous Quality Improvement: 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines Update for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care". Circulation. 132 (18 Suppl 2): S397-413. doi:10.1161/cir.0000000000000258. PMID 26472992. S2CID 10073267.