കിങ്ഡം
ടാക്സോണൊമിക് റാങ്ക്
ജീവശാസ്ത്രത്തിൽ ശാസ്ത്രീയ വർഗ്ഗീകരണത്തിലെ ഫൈലത്തിനും ഡൊമെയിനും ഇടയിൽ ഉള്ള വർഗ്ഗീകരണതലമാണ് കിങ്ഡം. വർഗ്ഗീകരണശാസ്ത്രത്തിലെ ഏറ്റവും ഉയർന്ന റാങ്ക് ആണ് ഇത്. കിംങ്ഡത്തിനെ ചെറിയ ഫൈലങ്ങൾ ആയി തിരിച്ചിരിക്കുന്നു.
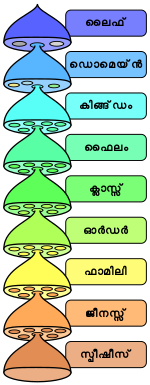
വിവിധ കിംങ്ഡങ്ങൾ തിരിച്ചുള്ള വർഗ്ഗീകരണത്തിന്റെ സംഗ്രഹം
തിരുത്തുക| കാൾ ലിനേയസ് 1735[1] |
Haeckel 1866[2] |
Chatton 1925[3][4] |
Copeland 1938[5][6] |
Whittaker 1969[7] |
Woese et al. 1977[8][9] |
Woese et al. 1990[10] |
Cavalier-Smith 1993[11][12][13] |
Cavalier-Smith 1998[14][15][16] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 kingdoms | 3 kingdoms | 2 empires | 4 kingdoms | 5 kingdoms | 6 kingdoms | 3 domains | 8 kingdoms | 6 kingdoms |
| (not treated) | Protista | Prokaryota | Monera | Monera | Eubacteria | Bacteria | Eubacteria | Bacteria |
| Archaebacteria | Archaea | Archaebacteria | ||||||
| Eukaryota | Protoctista | Protista | Protista | Eukarya | Archezoa | Protozoa | ||
| Protozoa | ||||||||
| Chromista | Chromista | |||||||
| Vegetabilia | Plantae | Plantae | Plantae | Plantae | Plantae | Plantae | ||
| Fungi | Fungi | Fungi | Fungi | |||||
| Animalia | Animalia | Animalia | Animalia | Animalia | Animalia | Animalia |
ഇതും കാണുക
തിരുത്തുകഅവലംബം
തിരുത്തുക- ↑ Linnaeus, C. (1735). Systemae Naturae, sive regna tria naturae, systematics proposita per classes, ordines, genera & species.
- ↑ Haeckel, E. (1866). Generelle Morphologie der Organismen. Reimer, Berlin.
- ↑ Chatton, É. (1925). "Pansporella perplexa. Réflexions sur la biologie et la phylogénie des protozoaires". Annales des Sciences Naturelles - Zoologie et Biologie Animale. 10-VII: 1–84.
- ↑ Chatton, É. (1937). Titres et Travaux Scientifiques (1906–1937). Sette, Sottano, Italy.
- ↑ Copeland, H. (1938). "The kingdoms of organisms". Quarterly Review of Biology. 13: 383–420. doi:10.1086/394568.
- ↑ Copeland, H. F. (1956). The Classification of Lower Organisms. Palo Alto: Pacific Books. doi:10.5962/bhl.title.4474.
- ↑ Whittaker, R. H. (1969). "New concepts of kingdoms of organisms". Science. 163 (3863): 150–60. doi:10.1126/science.163.3863.150. PMID 5762760.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Woese, C. R.; Balch, W. E.; Magrum, L. J.; Fox, G. E.; Wolfe, R. S. (1977). "An ancient divergence among the bacteria". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 9 (4): 305–311. doi:10.1007/BF01796092. PMID 408502.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Woese, C. R.; Fox, G. E. (1977). "Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 74 (11): 5088–90. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. PMC 432104. PMID 270744.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Woese, C.; Kandler, O.; Wheelis, M. (1990). "Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 87 (12): 4576–9. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87.4576W. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. PMC 54159. PMID 2112744.
- ↑ PMID 7337818 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 1302186 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 8302218 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ Cavalier-Smith, T. (1998), "A revised six-kingdom system of life", Biological Reviews, 73 (03): 203–66, doi:10.1111/j.1469-185X.1998.tb00030.x, PMID 9809012
- ↑ Cavalier-Smith, T. (2004), "Only six kingdoms of life" (PDF), Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B Biological Sciences, 271: 1251–62, doi:10.1098/rspb.2004.2705, PMC 1691724, PMID 15306349, retrieved 2010-04-29
- ↑ Cavalier-Smith T (2010). "Kingdoms Protozoa and Chromista and the eozoan root of the eukaryotic tree". Biol. Lett. 6 (3): 342–5. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2009.0948. PMC 2880060. PMID 20031978.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)